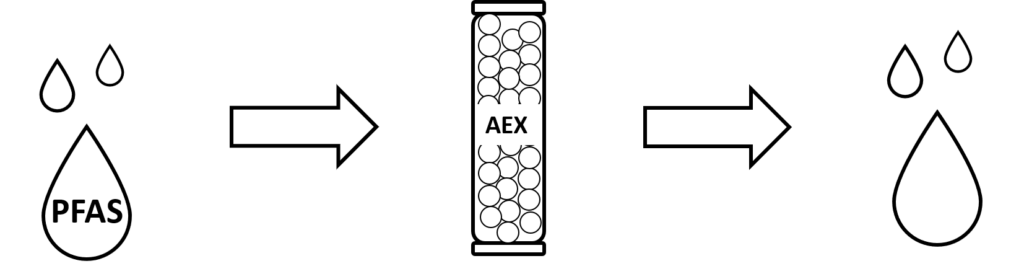
PFAS have been shown to be removed by anion exchange resins (AEX). The PFAS sorption mechanism into AEX resins is postulated to be based on a combination of ion, hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions. AEX has shown to have greater performance, better removal capacities and to be less impacted by organic matter, than the usually used granular activated carbon (GAC) filters. Furthermore, some of the AEX resins can be regenerated, whereas exhausted GAC resins are normally incinerated. Overall, AEX represents the option to design a more cost-efficient technology for PFAS removal than GAC. Within the LIFE SOuRCE project, AEX resins will be tested to remove PFAS after the SAFF treatment, as polishing step. The aim is to optimize the AEX filters operation according to the groundwater site characteristics.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |